Outer Barrier
| Part of a series on |
| Long Island |
|---|
 |
| Topics |
| Regions |
The Outer Barrier, also known as the Long Island and New York City barrier islands, refers to the string of barrier islands that divide the lagoons south of Long Island, New York from the Atlantic Ocean. These islands include Long Beach Barrier Island, Barnum Island, Jones Beach Island, Fire Island and Westhampton Island. The outer barrier extends 75 miles (121 km) along the South Shore of Long Island, from the Rockaway Peninsula in New York City to the east end of Shinnecock Bay in Suffolk County.
The lagoons enclosed by the barrier islands are Jamaica Bay, Brosewere Bay, Hewlett Bay, Reynolds Channel, Middle Bay, East Bay, South Oyster Bay, Great South Bay, and arms of the Great South Bay that have their own geographic names: Great Cove, Nicoll Bay, Patchogue Bay, Bellport Bay, Narrow Bay, Moriches Bay, Quantuck Bay, Tiana Bay, and Shinnecock Bay. East Rockaway Inlet, Jones Inlet, Fire Island Inlet, Old Inlet, Moriches Inlet, and Shinnecock Inlet pierce the barrier, forming the individual sandy islands. The resort communities of Atlantic Beach, Long Beach, and Westhampton Beach; the Fire Island National Seashore, Robert Moses State Park, Jones Beach State Park, and other recreational areas are found there. The low-lying islands are subject to wave erosion, and, during storms, they are sometimes inundated and cut through.[citation needed]
The islands
[edit]
New York City islands
[edit]Coney Island, Plumb Beach, Barren Island, several smaller islands in Jamaica Bay, and parts of what is now the Rockaway peninsula formerly comprised the westernmost Outer Barrier islands. Of these, Coney Island was the westernmost island. Most of these islands were either connected to mainland Long Island or combined with each other in the early 20th century.[1]
Long Beach Barrier Island
[edit]Long Beach Barrier Island lies off the south shore of Long Island. The island is shared by the hamlet of Atlantic Beach to the west, the city of Long Beach and the hamlet of Lido Beach in the central part of the island, and the hamlet of Point Lookout at the eastern end of the island. (The three hamlets — Atlantic Beach, Lido Beach, and Point Lookout — are part of the town of Hempstead, New York.)
Within its section of the barrier island, the city of Long Beach spans the entire north-south width of the island, fronting on both Reynolds Channel to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. A drawbridge, the Long Beach Bridge, connects it to Island Park, a small island which lies between Long Beach and the mainland of Long Island. To the west, the Atlantic Beach Bridge connects the island to Lawrence on Long Island. The Loop Parkway, located to the east where Lido Beach and Point Lookout border one another, connects the island to Jones Beach.

Jones Beach Island
[edit]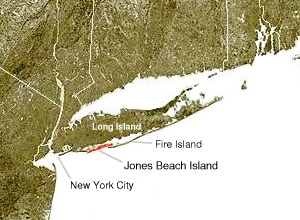
Jones Beach Island is a barrier island off the southern coast of Long Island in the U.S. state of New York. It is named for the father of historian Thomas Jones. It is sometimes referred to as Oak Beach Island, and the former home of the infamous Oak Beach Inn. It is separated from Long Island by Great South Bay. The island straddles the county line between Nassau and Suffolk counties and includes the census-designated places of Gilgo, Oak Beach, and Captree.
The southern side of the island is known for its beaches that face the open Atlantic Ocean. Jones Beach State Park, on the western tip of the island is a summer recreational destination for the New York City area.

It is accessible from Long Island on its western end by the Meadowbrook Parkway to Merrick, New York, the Loop Parkway to Long Beach, New York and the Wantagh Parkway to Wantagh, New York. Its eastern end is linked to Babylon, New York as well as to Fire Island, New York by the Robert Moses Causeway via the Great South Bay Bridge and the State Boat Channel Bridge. The Ocean Parkway connects all three causeways and runs the length of the island, while The Fire Island Inlet Bridge continues on the Robert Moses Causeway finding its way to the New York's Fire Island on the Atlantic Ocean.
Fire Island
[edit]Fire Island is a barrier island, approximately 31 miles (50 km) long and varying between approximately 0.1 mile (160 m) to 0.25 mile (400 m) wide. Fire Island passes through southern Suffolk County, New York, and is southeast of Long Island separated from the main land by the Great South Bay in the U.S. state of New York, running approximately SW to NE. The land area is 8.687 sq. mi. (22.5 km2), and a permanent population of 491 people was reported as of the 2000 census. (There are hundreds of thousands of summertime residents, groupers and daytrippers.) The island is composed of three communities, as defined by the Census Bureau. The largest of these is Fire Island (CDP), which is unincorporated and stretches through the southern portion of the towns of Babylon, Islip, and Brookhaven.
There are several ocean front communities such as, Davis Park and Watch Hill that are on the eastern side of the Great south bay. Fire Island has a variety of ocean front communities that can be reached by private boat, or seasonal ferry service from Long Island's mainland. Fire Island has a 2000 census population of 310 inhabitants. There are also two villages in the Islip section of the island, Saltaire (pop. 43) and Ocean Beach (pop. 138). In addition, a part of Fire Island CDP is not even on the island, but on a separate island adjacent to West Hampton Dunes.
Fire Island Inlet is an inlet on the south shore of Long Island, New York. It connects the Great South Bay with the Atlantic Ocean, passing between Robert Moses State Park (the western end of Fire Island) on the south and Oak Beach and Captree State Park (the eastern end of Jones Island) on the north. The stated land area and population figures result when this section is subtracted out.[2] The inlet is directly south of West Islip, the nearest town on the main part of Long Island.

The inlet has evolved over the years due to natural processes, especially longshore drift. Jones Island and Fire Island at one time were connected. The Fire Island Light was at the mouth of the inlet when built in 1858, but is now six miles east of the inlet.
Westhampton Island
[edit]Westhampton Island[3] is the easternmost outer barrier island in the Town of Southampton. The barrier island was part of Fire Island until a nor'easter in 1931 created Moriches Inlet and made Fire Island a proper island. The 1938 New England hurricane created Shinnecock Inlet and this Westhampton Island. Cupsogue Beach County Park is located on the western end of the island.

Moriches Inlet is an inlet connecting Moriches Bay and the Atlantic Ocean. The inlet created a geographic oddity whereby the Town of Brookhaven actually has jurisdiction on land immediately west of the village of West Hampton Dunes although Brookhaven land access to it involves a nearly 20 mile drive through Southampton.
Shinnecock Inlet is the easternmost of five major inlets[4] connecting bays to the Atlantic Ocean through the narrow 100-mile-long barrier islands that stretch from New York City to Southampton, New York on the south shore of Long Island.
The inlet was formed by the Great Hurricane of 1938 which killed several people when it permanently broke through the island in Hampton Bays, New York.
The inlet is almost directly lined up with the Shinnecock Canal between Shinnecock Bay and the Peconic Bay and saves miles for boaters going to the open Atlantic. Consequently, management has been geared to keep the inlet dredged and open. However, maintenance of the inlet has been controversial on grounds that it causes beach erosion on Fire Island.

See also
[edit]
- Ocean Parkway (Long Island)
- Robert Moses Causeway
- Robert Moses State Park (Long Island)
- Rockaway Inlet
References
[edit]- ^ Cody, Sarah K.; Auwaerter, John; Curry, George W. (2009). "Cultural Landscape Report for Floyd Bennett Field" (PDF). nps.gov. State University of New York, College of Environmental Science and Forestry: 16.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". Retrieved March 29, 2020.
- ^ "GNIS Detail - Westhampton Island".
- ^ "ADCIRC Example, Shinnecock Inlet". www.nd.edu. Archived from the original on January 3, 2005.
External links
[edit]- Captree State Park Archived September 24, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- Jones Beach State Park
- New York State Parks: Robert Moses State Park - Long Island Archived May 13, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Ocean Parkway article from Greater New York Roads Website Archived January 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Ocean Parkway article from NYCROADS Website

